Excvrとrust-analyzerでJupyterでRust
TL;DR
とりあえずRustを動かしてみたい、といった用途ではJupyterは非常に有用な環境です。
excvrを使うことでJupyter上でRustを使うことができるようになります。
また、jupyter-lspを使いrust-analyzerをJupyter上で動かせるようにすることで、開発体験を向上させます。
polarsと抱合せですが、以下のレポジトリで動作が確認できます。
excvr用のimageの作成
evcxr_jupyter自体のインストールは公式が詳しいです。
libzmq3-devがないとエラーしたので、加えてあります。
今回はevcxr_jupyterのインストールに加えて、jupyter-lab、jupyter-lsp、rust-analyzerのインストールを行っています。
Dockerfile
FROM rust:1.56 as rust
USER root
# 依存ライブラリのインストール
RUN apt-get update -y --fix-missing && \
apt-get install -y build-essential cmake jupyter-notebook libzmq3-dev
# evcxr_jupyterのインストール
RUN rustup component add rust-src && \
cargo install evcxr_jupyter && \
evcxr_jupyter --install
# pipのインストール
RUN wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py && \
python3 get-pip.py && rm -f get-pip.py && \
pip install jupyterlab && pip install -U jupyter_client
# lsp関連のインストール
RUN pip install jupyter-lsp jupyterlab-lsp && \
curl -L https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/releases/latest/download/rust-analyzer-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu.gz | \
gunzip -c - > /usr/local/bin/rust-analyzer && \
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/rust-analyzer
CMD [ "jupyter", "lab", "--port", "8888", "--ip=0.0.0.0", "--allow-root" ]
jupyter-lsp用の設定
pythonやrなど、jupyterでメジャーな言語のものは自動でlspを検出してくれるようですが、rustの場合は自前で設定を書く必要があります。
jupyter-lsp configuringのScalaの例を参考に設定ファイルを作成します。
以下のファイルをjupyter --pathsで表示されるディレクトリのどれか以下にjupyter_server_config.dを作成し、それ以下に配置します。
今回は${HOME}/.jupyter/jupyter_server_config.d/rust-analyzer.jsonというように配置します。
rust-analyzer.json
{
"LanguageServerManager": {
"language_servers": {
"rust-analyzer": {
"version": 2,
"argv": ["/usr/local/bin/rust-analyzer"],
"languages": ["rust"],
"mime_types": ["text/x-rust"]
}
}
}
}
docker-composeの設定
すでに書いたように、rust-analyzer.jsonを${HOME}/.jupyter/jupyter_server_config.d/rust-analyzer.jsonに配置します。
また、work以下をマウントして、ローカルと共有しています。
docker-compose.yaml
version: "3"
services:
jupyter:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
image: jupyter
environment:
- TZ=Asia/Tokyo
- JUPYTER_ENABLE_LAB=yes
ports:
- 8888:8888
volumes:
- ${PWD}/work:/work
- "${PWD}/jupyter_server_config.d:/root/.jupyter/jupyter_server_config.d"
working_dir: "/work"
Cargo.tomlの作成
rust-analyzer自体はCargoがないプロジェクトでも動かせるらしいですが(参考)、今回は面倒なので、Cargo.tomlを使ってdocker-compse.ymlで共有するためのworkディレクトリを作成します。
cargo new work
実行
これで、docker-compose upでjupyterが起動するはずです。
以下のように補完が効くようになります。
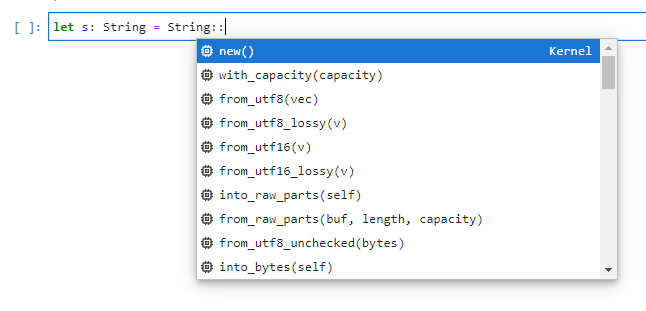
VSCodeほどではないですが、tab補完よりは快適な気がします。